 SOURCES, LANDMARKS AND HISTORIOGRAPHY OF DEVELOPMENT OF UKRAINIAN LAW
SOURCES, LANDMARKS AND HISTORIOGRAPHY OF DEVELOPMENT OF UKRAINIAN LAW
On 24-th of August 1991 a grand event took place in the history of Ukrainian people. That day the Verkhovna Rada of the Ukrainian republic adopted «Declaration of Independence of Ukraine». On the 1-st of December it was confirmed publicly at the All-Ukrainian referendum.
The new page of the revival of historical memory, consciousness and state-legal life of the Ukrainian people was opened. It is very difficult to understand modern processes and make fruitfully a new state; in its background should be the supremacy of law, justice and law, without deep comprehension of the millennial past in all its complication and irreconcilability.
In the time of universal reforms the interest to customs, traditions, law and history is increasing (growing) highly. It is accounted that law it is one of the most important tools, instruments, guides of ensuring of social equity, guaranties of realization of human rights and interests. Law is a part of people culture. Its learning historically exhorted to awaken, renew lost, raise to a much higher level personal legal sense as a part of the consciousness of people, who is the actual creator of its history.
Legal science of Ukraine has been developed complicated and contradicting as the whole history of Ukrainian people. It depended on those ideological positions, doctrines, which have been taking by the ruling circles of states, which contained several parts of Ukraine on the different stages of its development. Because of the narrow bounds, established by the authority it was difficult to extravagate for examiners of historiography, source study, ontology and gnosiology, phenomenology and axiology of law. For example, the whole power of Rech Pospolyta directed to the Polish influence of the Ukrainian people and the autocracy of Russia didn’t accept its individuality, calling it «maloross». Since the reign of Catherine II bureaucracy had to pursue such state policy to eliminate not even such notion as «Ukrainian», but also «Mala Russia», hetmans. Everything that reminded of Ukraine, its rights and liberties supposed to be the separatism and was punished cruelly by the government authority.
Almost since the rule of B. Hmelnitsky, especially since the reign of Peter I and Catherine II measures were taken to stop the development of national consciousness of Ukrainian people. Nor even works of the world-wide genius Shevchenko, neither «Gospel» were printed in Russian. Ukrainian Studies as a subject was removed from schools, secondary educational establishments and establishments of higher education of Ukraine, and even some branches of knowledge. Also it was forbidden in some educational institutions of Russia which had fallen within the history and culture of Ukraine.
Revolutions of 1917 changed real conditions of the development of Ukrainian people: it was the new stage of revival of its statehood and law, culture, national consciousness.
48
 For the first time in Ukraine it was provided for the research studies and teaching of Ukrainian law in its historical development in 1917, in the separate chair of Kyiv university. Because of the civil war it was impossible to develop its activity, all the more of emigration of the majority of professorate.
Scientific- practical conference of historians and theorists of law took place in Kharkiv in 1957. It admitted the necessity to include the special course of history of statehood and law of national republics to the curriculum of law schools.
During the last 70-th codes of laws and different compilations of statutes, especially government regulations, decrees of the Presidium of the Verkhovna Rada, shorthand records of the sessions of the Verkhovna Rada of the republic had been published constantly. Since publishing of the last years the most informative importance had «Systematic collection of current legislation of USSR» and «Code of statutes of Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic».
At present stage of the development of the Ukrainian Studies it needs by force of professional institutes of Academy of Science of Ukraine, law schools to provide with urgent necessities of scientific treatment problems of theory and history of national law, to increase the publication of current sources of Ukrainian law, monuments of legal culture, to publish the best researches of foreign scientists etc.
By the customary regulation it has been established the order of conclusion of exchange contracts, sales contracts, also the order to use common meadows, water, forest etc.
For the first time in Ukraine it was provided for the research studies and teaching of Ukrainian law in its historical development in 1917, in the separate chair of Kyiv university. Because of the civil war it was impossible to develop its activity, all the more of emigration of the majority of professorate.
Scientific- practical conference of historians and theorists of law took place in Kharkiv in 1957. It admitted the necessity to include the special course of history of statehood and law of national republics to the curriculum of law schools.
During the last 70-th codes of laws and different compilations of statutes, especially government regulations, decrees of the Presidium of the Verkhovna Rada, shorthand records of the sessions of the Verkhovna Rada of the republic had been published constantly. Since publishing of the last years the most informative importance had «Systematic collection of current legislation of USSR» and «Code of statutes of Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic».
At present stage of the development of the Ukrainian Studies it needs by force of professional institutes of Academy of Science of Ukraine, law schools to provide with urgent necessities of scientific treatment problems of theory and history of national law, to increase the publication of current sources of Ukrainian law, monuments of legal culture, to publish the best researches of foreign scientists etc.
By the customary regulation it has been established the order of conclusion of exchange contracts, sales contracts, also the order to use common meadows, water, forest etc.
 In the field of criminal law it is known such cases as private war, fire and water ordeal (so-called «Divine justice»), compensation for damaging words, assault and battery to the health or human honour, property etc.
In the customary law of the Eastern Slavs there was no division into separate institutions, especially as fields of law. In their legal awareness the notion of law combined for the most part with the notion of honesty and conscience, justice and brotherhood, equality and truth. All rules of conduct are recognized by one notion, «Law Rus».
In the conditions of powerful development and extension of international relations of Ukraine-Rus with other countries conventional rules could not satisfy the increasing requirements of social and political life. At the same time it has been appearing new law sources in the order of initiative development of princely legislation by the need of conclusion of interprincely and intergovernmental contracts and treaties.
In due course the process of legislation gets complicated: new statutes and prince’s lessons are proclaimed in towns, districts for the holidays. The most important of them are concentrated in the central authorities, formed and systematized compilations of legal norms.
In the field of criminal law it is known such cases as private war, fire and water ordeal (so-called «Divine justice»), compensation for damaging words, assault and battery to the health or human honour, property etc.
In the customary law of the Eastern Slavs there was no division into separate institutions, especially as fields of law. In their legal awareness the notion of law combined for the most part with the notion of honesty and conscience, justice and brotherhood, equality and truth. All rules of conduct are recognized by one notion, «Law Rus».
In the conditions of powerful development and extension of international relations of Ukraine-Rus with other countries conventional rules could not satisfy the increasing requirements of social and political life. At the same time it has been appearing new law sources in the order of initiative development of princely legislation by the need of conclusion of interprincely and intergovernmental contracts and treaties.
In due course the process of legislation gets complicated: new statutes and prince’s lessons are proclaimed in towns, districts for the holidays. The most important of them are concentrated in the central authorities, formed and systematized compilations of legal norms.
49
 At the same time the legal church situation in the state, priesthood and other church people was determined except by the Greek Church legal proposition also there was the princely legislation, which took legal shape of church regulations. From six statutes known today there were three which fell within the Ukrainian church: the prince’s Volodymyr Church Statutes, the prince’s Yaroslav Church Statutes and the prince’s Mstyslav Kyivsky Church Statutes. The main content of these princes’s comes to the determination of the church place in the state, subordinacy of church people of the Church court, church right to so-called «tithe».
At the same time the legal church situation in the state, priesthood and other church people was determined except by the Greek Church legal proposition also there was the princely legislation, which took legal shape of church regulations. From six statutes known today there were three which fell within the Ukrainian church: the prince’s Volodymyr Church Statutes, the prince’s Yaroslav Church Statutes and the prince’s Mstyslav Kyivsky Church Statutes. The main content of these princes’s comes to the determination of the church place in the state, subordinacy of church people of the Church court, church right to so-called «tithe».
 It is important for conception of Ukrainian law of that time there are legal internationality contracts that were concluded by the princes with foreign countries, especially with Greeks and Germans. In the ancient times international contracts based themselves principally on municipal law\ customs, traditions, statutes, laws\ and could make new forms of statutes, which reconciled some parts of inter-state agreement relations and had public nature.
Law of that time has not known the division into different branches, determined the strict limit between crime and civil offence, criminal law and civil law yet.
It is important for conception of Ukrainian law of that time there are legal internationality contracts that were concluded by the princes with foreign countries, especially with Greeks and Germans. In the ancient times international contracts based themselves principally on municipal law\ customs, traditions, statutes, laws\ and could make new forms of statutes, which reconciled some parts of inter-state agreement relations and had public nature.
Law of that time has not known the division into different branches, determined the strict limit between crime and civil offence, criminal law and civil law yet.
 Amid the crimes especially dangerous were encroachment on prince’s power, breaking faith, participation in revolt, crimes against the faith and church. The gravest and the most dangerous crimes against the personality were a murder, mutilation, slashing and batterery, property destruction. Farther on there were such kinds of crimes as contumeliousy, contempt, damaging of other’s property.
A proceeding formed historically and was adversarial-incriminating. Different parts in the lawsuit were equal, and therefore their collected physical evidence, witnesses and also conducted special investigation proceedings such as «persecution track», «code» and others by themselves.
It is known that the successor of Kievan Rus in Ukraine was the Galicia-Volyn principality — the state, whose formation dates refer to the second half of the 11th century.
In addition to separate sources of local law, in Ukraine there act and were effective normative acts of foreign extraction, including Law Code of Casimir of 1468, — at the same time both the Polish king and the grand Lithuanian prince, Sejm decrees and constitutions of Rich Pospolyta such as «Ustav na Voloki» 1557, «The Lithuanian Statute» three editions (1529, 1566, 1588), differ
ent re-makings of collection of urban self-government rights (so called Magdeburg law), «Zertsalo of Saxons» etc.
Amid the crimes especially dangerous were encroachment on prince’s power, breaking faith, participation in revolt, crimes against the faith and church. The gravest and the most dangerous crimes against the personality were a murder, mutilation, slashing and batterery, property destruction. Farther on there were such kinds of crimes as contumeliousy, contempt, damaging of other’s property.
A proceeding formed historically and was adversarial-incriminating. Different parts in the lawsuit were equal, and therefore their collected physical evidence, witnesses and also conducted special investigation proceedings such as «persecution track», «code» and others by themselves.
It is known that the successor of Kievan Rus in Ukraine was the Galicia-Volyn principality — the state, whose formation dates refer to the second half of the 11th century.
In addition to separate sources of local law, in Ukraine there act and were effective normative acts of foreign extraction, including Law Code of Casimir of 1468, — at the same time both the Polish king and the grand Lithuanian prince, Sejm decrees and constitutions of Rich Pospolyta such as «Ustav na Voloki» 1557, «The Lithuanian Statute» three editions (1529, 1566, 1588), differ
ent re-makings of collection of urban self-government rights (so called Magdeburg law), «Zertsalo of Saxons» etc.
50

 All sources of law acted in reciprocity, sometimes to put standards of urban law into the foundation of causes’ consideration.
Famous Ukrainian academic scientist D. Bataliy affirmed that there were not even two cities in Ukraine where the sum of the Magdeburg laws was the same and that was the reason to give the city all rights for self-government and significance of the city.
In the Middle Dnieper regions, so called Cossacks and their battle centre the Zaporizhian Sich, has appeared as the result of reinforcement of socio-economic, political and legal, and national-religious oppression of Ukrainians.
Cossacks’ self-acting, as the whole system of organs of military and administrative government had the opportunity to act and provide such inner and outside functions which are peculiar and inherent for state.
People’s Liberation War in 1648–1654 allowed forming the most important stage of revival of national statehood in Ukraine.
During the revival of national statehood in Ukraine there appeared distinctive system of law and court, the foundation of which was the customary law of Zaporizhian Sich, especially those standards of this law, which during the People’s Liberation War regulated military and administrative organization and administration, rights and duties of Cossack officers, legal procedure etc.
At the same time the customary law of Zaporizhian Sich was supplemented by acts of the law of local military and administrative government, as far as it was considered national law and it was the most prestige among people, and was protected by government and national rites, traditions and even got specific name «Cossack law». Also it completely formed ambushes for the future and became the basis of Hetman law.
Despite the complexity and contradiction of real legal status in Ukraine as a part of Russia, Hetman legal system existed until 1840–1842 years.
At that time a lot of regulations were out of date and often contradicted each other, duplicated specific legal provisions etc. The main concern was that the actual legal system Hetman did not only match, but sometimes even contradicted to the legal system of Russia, its imperial claims.
Also we should notice the fact that social order landowners Hetman was done most fully and carefully only during the second official codification of 1750–1758 years, when on the instruction of hetman K. Rozumovsky candidate members of the General Military Court F. Chuykevych worked out collection of legal norms and legal proceedings under the title «Judgment and punishment in the Little Russian rights».
In history of Ukraine law there are two very similar in form but very opposite to the content of legal interest.
All sources of law acted in reciprocity, sometimes to put standards of urban law into the foundation of causes’ consideration.
Famous Ukrainian academic scientist D. Bataliy affirmed that there were not even two cities in Ukraine where the sum of the Magdeburg laws was the same and that was the reason to give the city all rights for self-government and significance of the city.
In the Middle Dnieper regions, so called Cossacks and their battle centre the Zaporizhian Sich, has appeared as the result of reinforcement of socio-economic, political and legal, and national-religious oppression of Ukrainians.
Cossacks’ self-acting, as the whole system of organs of military and administrative government had the opportunity to act and provide such inner and outside functions which are peculiar and inherent for state.
People’s Liberation War in 1648–1654 allowed forming the most important stage of revival of national statehood in Ukraine.
During the revival of national statehood in Ukraine there appeared distinctive system of law and court, the foundation of which was the customary law of Zaporizhian Sich, especially those standards of this law, which during the People’s Liberation War regulated military and administrative organization and administration, rights and duties of Cossack officers, legal procedure etc.
At the same time the customary law of Zaporizhian Sich was supplemented by acts of the law of local military and administrative government, as far as it was considered national law and it was the most prestige among people, and was protected by government and national rites, traditions and even got specific name «Cossack law». Also it completely formed ambushes for the future and became the basis of Hetman law.
Despite the complexity and contradiction of real legal status in Ukraine as a part of Russia, Hetman legal system existed until 1840–1842 years.
At that time a lot of regulations were out of date and often contradicted each other, duplicated specific legal provisions etc. The main concern was that the actual legal system Hetman did not only match, but sometimes even contradicted to the legal system of Russia, its imperial claims.
Also we should notice the fact that social order landowners Hetman was done most fully and carefully only during the second official codification of 1750–1758 years, when on the instruction of hetman K. Rozumovsky candidate members of the General Military Court F. Chuykevych worked out collection of legal norms and legal proceedings under the title «Judgment and punishment in the Little Russian rights».
In history of Ukraine law there are two very similar in form but very opposite to the content of legal interest.
51

 This is «The extract of Little Russian rights» which was worked out on the instruction of governor of Little Russia P. Rumiantseva, Little Board secretary O. Bezborodko in 1767 and «The extract of the decrees, regulations and institutions … Senate» of Russia in 1786.
In the last decade of the 17th century abolished by Catherine II and restored by Paul I «prior law on the judiciary and judicial proceedings outdated in Ukraine, that’s why they did not correspond its colonial situation in the Russian Empire and new conditions of socio-economical development of society.
Attempts at reforming the law of Ukraine and the whole empire has occurred in the first half of the 19th century. But they actually have already broken against the imperial policy of Alexander I and Nicholas I, who ruled the country «on the model rules of Grandmother Catherine» strictly looking at the fact that not only the letter but the spirit of her legislation were not changed.
In the period of formation of a unified legal system of the Russian Empire in 1840 in Ukraine was extended operation of law «Code Laws Empire» first, and in 1842 — the second version of the same Code. During 1824–183 5 was abolished action of Magdeburg law and implemented in urban management and proceedings of the imperial «Charter cities» 1875.
For the development rights of Galicia, Northern Bukovina and Transcarpathia affected their being a part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. In 1753 in Austria it has already been created a special commission that was supposed to take steps to unify the empire right to liquidate its particularism, to develop a unified empire codes for different spheres of justice. For approval new codes in Galicia and Bukovina there operated customary law and sources of Polish law.
Since the late 17th century, at first in Galicia and later throughout the empire there began its criminal code in 1787, and since 1788 — the statute of criminal crimes. Present criminal code provided for severe punishment as death by hanging and the procedural code had the inquisitorial nature of the process, without a lawyer. Sentences were considered final and performed no later than 24 hours after their removal. These were the so-called «sudden courts».
The autocracy was eliminated after the victory of the bourgeois-democratic revolution in February 1917.
Therefore, 4 ( 17) March, 1917 there took place the Congress with representatives of the revolutionary parties, social movements, institutions and societies, which created the Central Council — nationwide coordination center. M. Hrushevsky, famous scientist and public-political figure, was elected as a chairman by the Central Council.
Proclamation of an independent Ukrainian National Republic was an extremely important decision and of course, it was noticeable in international relations. That’s why Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria and Turkey immediately concluded a peace agreement with Ukraine on January 14 ( 27), 1918. Also, sovereign Ukrainian state was recognized by such powerful states like Britain, France, USA, Japan, China, Finland, Poland, Romania, and later — Hungary, Czechoslovakia, the Vatican and other countries in the world. To keep the authority the Central Council requested military assistance from Germany and Austria-Hungary. But the revolution turned into a civil war, which was complicated by the intervention of outside powers — Germany and the states of Atlanta from the West and Soviet Russia — from the East.
The legal system of Western People’s Republic was defined by the law from November 21, 1918. Judicial functions were performed by county circuit courts and Supreme Court.
The legal system of the Soviet Ukraine began to form from the day of its proclamation, virtually from the day of the first All-Ukrainian Soviet Congress of Workers, Peasants and Soldiers’ Deputies. Basic rights have been secured by the Constitution of the USSR in 1919.
But with the entry of Ukraine into the USSR in the next years, especially in strengthening the administrative-command system
of centralized management, national moments in the development of law has already ceased to be counted.
This is «The extract of Little Russian rights» which was worked out on the instruction of governor of Little Russia P. Rumiantseva, Little Board secretary O. Bezborodko in 1767 and «The extract of the decrees, regulations and institutions … Senate» of Russia in 1786.
In the last decade of the 17th century abolished by Catherine II and restored by Paul I «prior law on the judiciary and judicial proceedings outdated in Ukraine, that’s why they did not correspond its colonial situation in the Russian Empire and new conditions of socio-economical development of society.
Attempts at reforming the law of Ukraine and the whole empire has occurred in the first half of the 19th century. But they actually have already broken against the imperial policy of Alexander I and Nicholas I, who ruled the country «on the model rules of Grandmother Catherine» strictly looking at the fact that not only the letter but the spirit of her legislation were not changed.
In the period of formation of a unified legal system of the Russian Empire in 1840 in Ukraine was extended operation of law «Code Laws Empire» first, and in 1842 — the second version of the same Code. During 1824–183 5 was abolished action of Magdeburg law and implemented in urban management and proceedings of the imperial «Charter cities» 1875.
For the development rights of Galicia, Northern Bukovina and Transcarpathia affected their being a part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. In 1753 in Austria it has already been created a special commission that was supposed to take steps to unify the empire right to liquidate its particularism, to develop a unified empire codes for different spheres of justice. For approval new codes in Galicia and Bukovina there operated customary law and sources of Polish law.
Since the late 17th century, at first in Galicia and later throughout the empire there began its criminal code in 1787, and since 1788 — the statute of criminal crimes. Present criminal code provided for severe punishment as death by hanging and the procedural code had the inquisitorial nature of the process, without a lawyer. Sentences were considered final and performed no later than 24 hours after their removal. These were the so-called «sudden courts».
The autocracy was eliminated after the victory of the bourgeois-democratic revolution in February 1917.
Therefore, 4 ( 17) March, 1917 there took place the Congress with representatives of the revolutionary parties, social movements, institutions and societies, which created the Central Council — nationwide coordination center. M. Hrushevsky, famous scientist and public-political figure, was elected as a chairman by the Central Council.
Proclamation of an independent Ukrainian National Republic was an extremely important decision and of course, it was noticeable in international relations. That’s why Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria and Turkey immediately concluded a peace agreement with Ukraine on January 14 ( 27), 1918. Also, sovereign Ukrainian state was recognized by such powerful states like Britain, France, USA, Japan, China, Finland, Poland, Romania, and later — Hungary, Czechoslovakia, the Vatican and other countries in the world. To keep the authority the Central Council requested military assistance from Germany and Austria-Hungary. But the revolution turned into a civil war, which was complicated by the intervention of outside powers — Germany and the states of Atlanta from the West and Soviet Russia — from the East.
The legal system of Western People’s Republic was defined by the law from November 21, 1918. Judicial functions were performed by county circuit courts and Supreme Court.
The legal system of the Soviet Ukraine began to form from the day of its proclamation, virtually from the day of the first All-Ukrainian Soviet Congress of Workers, Peasants and Soldiers’ Deputies. Basic rights have been secured by the Constitution of the USSR in 1919.
But with the entry of Ukraine into the USSR in the next years, especially in strengthening the administrative-command system
of centralized management, national moments in the development of law has already ceased to be counted.
52
 New direction and forms of law in Ukraine determined the effects of long scientific debate in the 50 s.
On the basis of the adopted and enacted legislation in the 60–70s years there was held the second general codification of Ukraine law, that had resulted in the creation of new codes of the Republic, which in the late 70’s — early 80’s were brought into compliance with new provisions of the Constitution of the USSR in 1977 and the Constitution of the Republic USSR in 1978.
Ukrainian law on the present stage of development (from 1990 till 2010)
New direction and forms of law in Ukraine determined the effects of long scientific debate in the 50 s.
On the basis of the adopted and enacted legislation in the 60–70s years there was held the second general codification of Ukraine law, that had resulted in the creation of new codes of the Republic, which in the late 70’s — early 80’s were brought into compliance with new provisions of the Constitution of the USSR in 1977 and the Constitution of the Republic USSR in 1978.
Ukrainian law on the present stage of development (from 1990 till 2010)
 Present stage of revival of national Ukrainian law relates to the first free elections of urban Councils and Verkhovna Rada, which were in March 1990. Thus, it was formed new parliament, which later began to take into its hands all economical and political power and became firmly established as the only legislative organ of URSR.
Democratic bloc of public organizations got approximately quarter (from 450) mandates in Verkhovna Rada and on July 16th, 1990 won prominent victory in parliament. According to its initiative Vekhovna Rada signed «Declaration about state sovereignty of Ukraine»; as the result of this action the state sovereignty was proclaimed as the supremacy, independence, plenitude and indivisibility of power of Republic within the limits of her territory, independence and equality in its external relations.
«People of Ukraine, — declares this legal act, — are the only source of state power in Republic. State power accomplishes by the principle of her dividing into legislative, executive and judicial. Any violent actions against the national state system of Ukraine from the side of political parties, public organizations, other groupments or individuals are pursued on a law. The state of Ukraine acknowledges advantage of common to all mankind values above class, priority of confessedly norms of international law above norms of domestic right. Declaration, which is underlined in a final part of act, is a foundation for new Constitution, different laws of Ukraine and determines positions of Republic at the mode of international agreements».
Declaration from July 16th, 1990 is a foundation for development of current legislation and forming of new legal system of Ukraine.
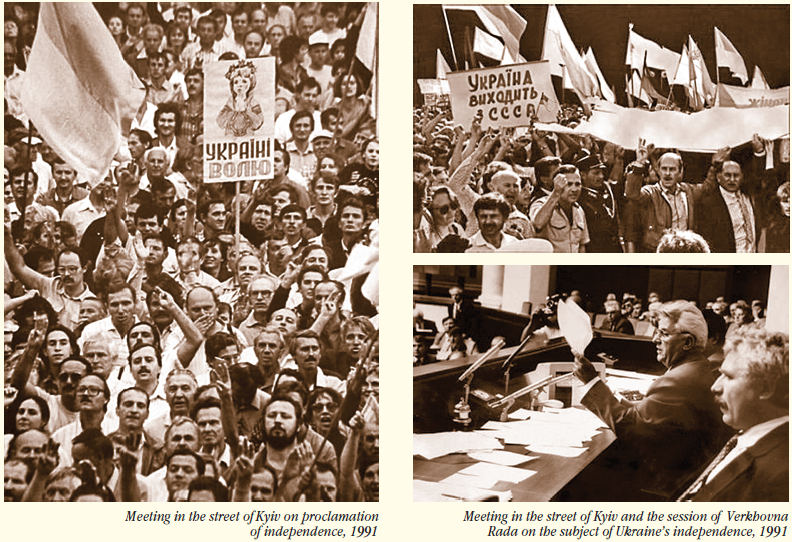
The attempt of putsch on August 18–21, 1991 accelerated disintegration of the USSR, but it did not influence on the change of the accepted course of democratic transformations in Ukraine. «As well as before, — declared on Ukrainian TV future president of Ukraine L. Kuchma, — we must go on the way of democracy, legality, law and order, observance of constitutional norms».
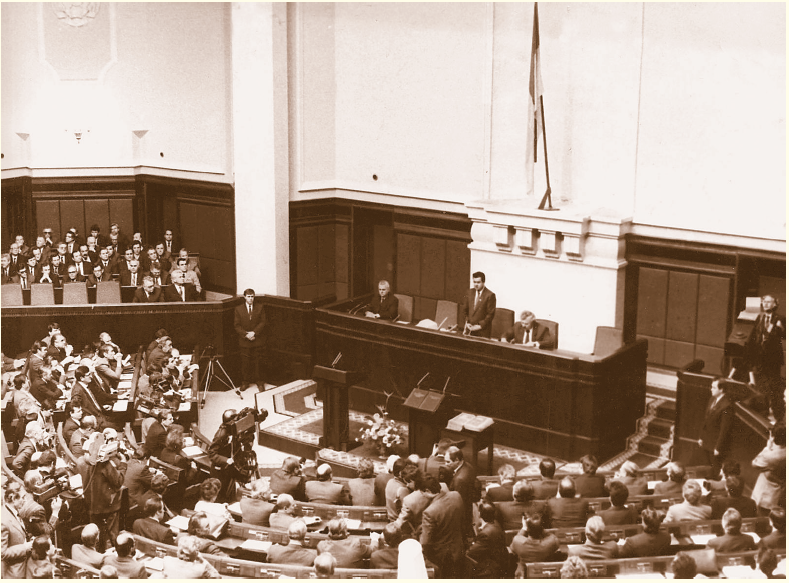
Expressing will of people, Verkhovna Rada of Respublic on August 24th, 1991 signed «Act of proclamation of independence of Ukraine». Where, in particular, it is indicated: «… — on self-determination, foreseen by UN Charter and other international documents, — realizing the “Declaration about state sovereignty of Ukraine», Vekhovna Rada proclaimed the independence of Ukraine and creation of independent Ukrainian state — Ukraine, the territory of which is indivisible and inviolable. From this time, — the act concluded, — on the territory of Ukraine operate exceptionally Constitution and laws of Ukraine.
Present stage of revival of national Ukrainian law relates to the first free elections of urban Councils and Verkhovna Rada, which were in March 1990. Thus, it was formed new parliament, which later began to take into its hands all economical and political power and became firmly established as the only legislative organ of URSR.
Democratic bloc of public organizations got approximately quarter (from 450) mandates in Verkhovna Rada and on July 16th, 1990 won prominent victory in parliament. According to its initiative Vekhovna Rada signed «Declaration about state sovereignty of Ukraine»; as the result of this action the state sovereignty was proclaimed as the supremacy, independence, plenitude and indivisibility of power of Republic within the limits of her territory, independence and equality in its external relations.
«People of Ukraine, — declares this legal act, — are the only source of state power in Republic. State power accomplishes by the principle of her dividing into legislative, executive and judicial. Any violent actions against the national state system of Ukraine from the side of political parties, public organizations, other groupments or individuals are pursued on a law. The state of Ukraine acknowledges advantage of common to all mankind values above class, priority of confessedly norms of international law above norms of domestic right. Declaration, which is underlined in a final part of act, is a foundation for new Constitution, different laws of Ukraine and determines positions of Republic at the mode of international agreements».
Declaration from July 16th, 1990 is a foundation for development of current legislation and forming of new legal system of Ukraine.
The attempt of putsch on August 18–21, 1991 accelerated disintegration of the USSR, but it did not influence on the change of the accepted course of democratic transformations in Ukraine. «As well as before, — declared on Ukrainian TV future president of Ukraine L. Kuchma, — we must go on the way of democracy, legality, law and order, observance of constitutional norms».
Expressing will of people, Verkhovna Rada of Respublic on August 24th, 1991 signed «Act of proclamation of independence of Ukraine». Where, in particular, it is indicated: «… — on self-determination, foreseen by UN Charter and other international documents, — realizing the “Declaration about state sovereignty of Ukraine», Vekhovna Rada proclaimed the independence of Ukraine and creation of independent Ukrainian state — Ukraine, the territory of which is indivisible and inviolable. From this time, — the act concluded, — on the territory of Ukraine operate exceptionally Constitution and laws of Ukraine.
53
 In new conditionals of alteration of economy of Ukraine, creating new national independent state, Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine conducts wide scale, legislative activity; more clearly determines the legal system of new society.
In this work an important value had «The law about legal continuity of Ukraine», accepted on September 12th, 1991. Before acceptance of new Constitution of Ukraine, in this law was determined that on the territory o f Ukraine operates Constitution (main law) of URSR. Laws of URSR and other acts, accepted by Verkhovna Rada of URSR, operate on the territory of Ukraine, as they do not contradict laws, which were signed after proclamation of independence of Ukraine. Ukraine confirmed its duties on the international agreements of the USSR, if they do not contradict with the Constitution of Ukraine and interests of republic. Independent Ukraine does not take the responsibility on credit agreements made without its consent after July 1st, 1991.
In relation to the legislation of the USSR Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine by a decision from September 12th, 1991 «About order of temporal action on territory of Ukraine of separate acts of legislation of the USSR» set that to the acceptance of corresponding acts of legislation of Ukraine on the territory of republic are applied the acts of legislation of the USSR on questions that are not well-regulated by the legislation of Ukraine, on condition that they do not contradict with a Constitution and laws of Ukraine.
Thus, at that time were formed the newest visible lines of modern national legal system of Ukraine. Today it continues to create farther. That’s great that Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine at this time takes under its jurisdiction everything that belongs to the sovereign state, beginning with borders, army, creating new laws on earth, entrepreneurial activity, human rights and surrounds its environment. Certainly, the process of lawmaking requires clearer, considered decision. As the result of this, Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine creates the law with important, but not always near-term problems of alteration of life of society and creation of legal state of Ukraine.
New age of 19th century requires new approaches and high quality of law-making, adoption of such laws which must assert and provide supremacy of right, justice, legality and other ideals of new generation of the Ukrainian people. Thus, on the stage of Ukrainian creation of the state, it was made right and effective beginning.
Gnosiological and view-methodological principles of realization of ideas of the legal state in Ukraine
Analysis of current legal system, legislation and development of state-building processes in Ukraine since independence (1991–2011 — almost 20 years), it shows us that in state is begun the process of forming of constitutionally-legal principles and mechanisms of development of social and legal state. Among the most meaningful achievements in the sphere of state-building activity there are:
revival of liberal-democratic traditions of constitutionalism (art. 1–68 Constitution of Ukraine);
laying the foundation of parliamentarism (art. 75–101 Constitution of Ukraine);
realization of principle of distribution of power (art. 6 Constitution of Ukraine);
process of reformation of the judicial system (art. 124–131 Constitution of Ukraine);
realization of transformation of the national system of legislation;
forming of positive tendencies in the estimation of human rights and freedoms and their protection
Restructuring (just with grave disadvantages and problems) of electoral laws;
Formation of Constitutional Court, Higher Council of Justice, setting as principle of legal platform and machineries of national security, activity of judicial proceeding, armed forces and protection of state borders;
Formation of foundations for public organization functioning, movements, television, non-state security service as basic elements of civil society.
Certainly this list can be continued, but main task for us today is to consolidate existing process, to develop and improve conceptions, doctrines, ideas, laws, other institutes and provide for real machineries of formation of legal state. Everyone has to understand that it is impossible to form a legal state, coming only to nothing more than adoption of laws.
Main problems of forming legal state in Ukraine come to that under conditions of pluralism of opinions, ideologies, changing of elites and power — sense and content of legal state idea can disagree fundamentally and even interpret in a different way, but of course it is not promote for harmonious state development. That’s why it should be promoted of the development of statehood in Ukraine.
At the same time principal things are permanent — Ukrainian legal state in spite of its special features, keeping its statehood. And it means that:
It does not identify with society and another system of special-political organization;
Except its own, specific features it has general signs;
It is committed with public authority, and it is an official representative of all social stratums;
It has apparatus of administration and coercion ;
It has system of legal measures in contrast to non-state organizations;
It has sovereignty that is shown in its supremacy concerning all another non-state organizations and all citizens.
All listed signs and features hereinbefore are general for any state, which are typical only for social, legal state. Among such distinctive important settings and guides the most important, in our opinion, are:
Right as a measure of equality, justice and liberty that dominates in all spheres of society;
Law acts not only for citizens but for all officers, government employees, organs and institutions of state authority and municipal government, while the country as a whole;
state authority functions on a footing of Constitution of Ukraine and effects by the principle of its division into legislative, executive and judicial authorities and it is implemented on the basis of functioning of “system of checks and balances” among them;
Rights, liberties and individual interests are indefeasible, and state guarantees their realization and secures them;
There is a reciprocal state and person responsibility;
Organized effective monitoring of legality (laws, decrees, regulations, instructions, orders etc);
highly effective activity of law enforcement and law courts to enforce rule of law, ensure the protection of human rights and liberties;
solution of conflicts and controversial questions only in court instances because the justice is accomplished only by law courts in Ukraine.
In new conditionals of alteration of economy of Ukraine, creating new national independent state, Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine conducts wide scale, legislative activity; more clearly determines the legal system of new society.
In this work an important value had «The law about legal continuity of Ukraine», accepted on September 12th, 1991. Before acceptance of new Constitution of Ukraine, in this law was determined that on the territory o f Ukraine operates Constitution (main law) of URSR. Laws of URSR and other acts, accepted by Verkhovna Rada of URSR, operate on the territory of Ukraine, as they do not contradict laws, which were signed after proclamation of independence of Ukraine. Ukraine confirmed its duties on the international agreements of the USSR, if they do not contradict with the Constitution of Ukraine and interests of republic. Independent Ukraine does not take the responsibility on credit agreements made without its consent after July 1st, 1991.
In relation to the legislation of the USSR Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine by a decision from September 12th, 1991 «About order of temporal action on territory of Ukraine of separate acts of legislation of the USSR» set that to the acceptance of corresponding acts of legislation of Ukraine on the territory of republic are applied the acts of legislation of the USSR on questions that are not well-regulated by the legislation of Ukraine, on condition that they do not contradict with a Constitution and laws of Ukraine.
Thus, at that time were formed the newest visible lines of modern national legal system of Ukraine. Today it continues to create farther. That’s great that Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine at this time takes under its jurisdiction everything that belongs to the sovereign state, beginning with borders, army, creating new laws on earth, entrepreneurial activity, human rights and surrounds its environment. Certainly, the process of lawmaking requires clearer, considered decision. As the result of this, Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine creates the law with important, but not always near-term problems of alteration of life of society and creation of legal state of Ukraine.
New age of 19th century requires new approaches and high quality of law-making, adoption of such laws which must assert and provide supremacy of right, justice, legality and other ideals of new generation of the Ukrainian people. Thus, on the stage of Ukrainian creation of the state, it was made right and effective beginning.
Gnosiological and view-methodological principles of realization of ideas of the legal state in Ukraine
Analysis of current legal system, legislation and development of state-building processes in Ukraine since independence (1991–2011 — almost 20 years), it shows us that in state is begun the process of forming of constitutionally-legal principles and mechanisms of development of social and legal state. Among the most meaningful achievements in the sphere of state-building activity there are:
revival of liberal-democratic traditions of constitutionalism (art. 1–68 Constitution of Ukraine);
laying the foundation of parliamentarism (art. 75–101 Constitution of Ukraine);
realization of principle of distribution of power (art. 6 Constitution of Ukraine);
process of reformation of the judicial system (art. 124–131 Constitution of Ukraine);
realization of transformation of the national system of legislation;
forming of positive tendencies in the estimation of human rights and freedoms and their protection
Restructuring (just with grave disadvantages and problems) of electoral laws;
Formation of Constitutional Court, Higher Council of Justice, setting as principle of legal platform and machineries of national security, activity of judicial proceeding, armed forces and protection of state borders;
Formation of foundations for public organization functioning, movements, television, non-state security service as basic elements of civil society.
Certainly this list can be continued, but main task for us today is to consolidate existing process, to develop and improve conceptions, doctrines, ideas, laws, other institutes and provide for real machineries of formation of legal state. Everyone has to understand that it is impossible to form a legal state, coming only to nothing more than adoption of laws.
Main problems of forming legal state in Ukraine come to that under conditions of pluralism of opinions, ideologies, changing of elites and power — sense and content of legal state idea can disagree fundamentally and even interpret in a different way, but of course it is not promote for harmonious state development. That’s why it should be promoted of the development of statehood in Ukraine.
At the same time principal things are permanent — Ukrainian legal state in spite of its special features, keeping its statehood. And it means that:
It does not identify with society and another system of special-political organization;
Except its own, specific features it has general signs;
It is committed with public authority, and it is an official representative of all social stratums;
It has apparatus of administration and coercion ;
It has system of legal measures in contrast to non-state organizations;
It has sovereignty that is shown in its supremacy concerning all another non-state organizations and all citizens.
All listed signs and features hereinbefore are general for any state, which are typical only for social, legal state. Among such distinctive important settings and guides the most important, in our opinion, are:
Right as a measure of equality, justice and liberty that dominates in all spheres of society;
Law acts not only for citizens but for all officers, government employees, organs and institutions of state authority and municipal government, while the country as a whole;
state authority functions on a footing of Constitution of Ukraine and effects by the principle of its division into legislative, executive and judicial authorities and it is implemented on the basis of functioning of “system of checks and balances” among them;
Rights, liberties and individual interests are indefeasible, and state guarantees their realization and secures them;
There is a reciprocal state and person responsibility;
Organized effective monitoring of legality (laws, decrees, regulations, instructions, orders etc);
highly effective activity of law enforcement and law courts to enforce rule of law, ensure the protection of human rights and liberties;
solution of conflicts and controversial questions only in court instances because the justice is accomplished only by law courts in Ukraine.
54
 At the same time, further development of legal state in Ukraine should continue to realize by the way of formed transformations and in the majority of formal features, in other words to be implemented in fundamental ideological creative principles. Among the most significant and actual directions of such perspective are:
The formation of civil society as a foundation of legal state. The civil society can ensure free and comprehensive development of personality, functioning of public institutions, free accession to the information, election, opposition, multi-party system etc.
Fundamental achievements of scientists in the field of law affirm that only civil society can oppose to the criminalized and corrupted in all society, processes of the usurpation of power, confrontation of democratic processes.
The construction of legal state is linked objectively with consolidation of democratic processes, reforms and traditions of functioning of power in Ukraine, in as much as the embodiment of democratic principles forms precondition of social equality and justice. At the same time democratic traditions in Ukraine which are been forming, still feeble and their fixing and development are prolonged and very important process for a person, authority and society. The pledge of these processes is a preservation of free election, formation of democratic political regime, liberty of mass media, clarity and farsightedness of politicians, patriotism, devotion to the national idea, preservation and revival of national customs, traditions, spirituality, social heritage etc, which will become almost the most important pledge of development of harmonious legal state in the near future.
Development of legal state depends directly on the level, range, systemic economic policy and state creative reforms.
At the same time, further development of legal state in Ukraine should continue to realize by the way of formed transformations and in the majority of formal features, in other words to be implemented in fundamental ideological creative principles. Among the most significant and actual directions of such perspective are:
The formation of civil society as a foundation of legal state. The civil society can ensure free and comprehensive development of personality, functioning of public institutions, free accession to the information, election, opposition, multi-party system etc.
Fundamental achievements of scientists in the field of law affirm that only civil society can oppose to the criminalized and corrupted in all society, processes of the usurpation of power, confrontation of democratic processes.
The construction of legal state is linked objectively with consolidation of democratic processes, reforms and traditions of functioning of power in Ukraine, in as much as the embodiment of democratic principles forms precondition of social equality and justice. At the same time democratic traditions in Ukraine which are been forming, still feeble and their fixing and development are prolonged and very important process for a person, authority and society. The pledge of these processes is a preservation of free election, formation of democratic political regime, liberty of mass media, clarity and farsightedness of politicians, patriotism, devotion to the national idea, preservation and revival of national customs, traditions, spirituality, social heritage etc, which will become almost the most important pledge of development of harmonious legal state in the near future.
Development of legal state depends directly on the level, range, systemic economic policy and state creative reforms.
 It is necessary to finish constitutional reform in the society on a legal footing to guarantee its implementation arrangements and in such way to paragraph about its violation in adoption of any law (tax code, labour code or other normative act). It is necessary to remedy through a referendum a polity in Ukraine, to pass the law on the responsibility of President, government, deputies of all levels; to conduct wide discussions about their sense, results etc. It needs honestly, openly, objectively to inform population about real, economic, financial, political, secure situation in the country. The authority must be politically responsible for non-professional actions of government officials, their decision-making and results. Legal state it is not only democratic but also social and sovereign country.
Legal state, it is first of all constitutional state.
Constitution of Ukraine — is the main law of legal state, it is a general, legal, moral model of society. No one other law, code, normative act should not and cannot contradict with Constitution of Ukraine, to create collisions in current legislation, but if it take such place — such legal document should not be adopted, and the adopted one should be abolished immediately as illegal, that contradicts with effective Constitution of Ukraine. The priority of Constitution of Ukraine is an integral part of legal state, and Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine, President of Ukraine, Constitutional Court, government and judicial authority are in responsible for this.
And, the last one. In spite of democratic and legal customs and traditions in Ukraine are not strong enough, but there are grave historical cultural traditions, heritage, achievements and also appropriate level of people consciousness, desire to build European state, to carry out other positive, irreversible, proactive processes — all these give reasons to affirm that strong legal state will be built in Ukraine.
Legal state in Ukraine, it is objectively necessary form of organization of legal system and functioning of power, individual and various unions, institutions of society on the basis of law, legality and justice.
It is necessary to finish constitutional reform in the society on a legal footing to guarantee its implementation arrangements and in such way to paragraph about its violation in adoption of any law (tax code, labour code or other normative act). It is necessary to remedy through a referendum a polity in Ukraine, to pass the law on the responsibility of President, government, deputies of all levels; to conduct wide discussions about their sense, results etc. It needs honestly, openly, objectively to inform population about real, economic, financial, political, secure situation in the country. The authority must be politically responsible for non-professional actions of government officials, their decision-making and results. Legal state it is not only democratic but also social and sovereign country.
Legal state, it is first of all constitutional state.
Constitution of Ukraine — is the main law of legal state, it is a general, legal, moral model of society. No one other law, code, normative act should not and cannot contradict with Constitution of Ukraine, to create collisions in current legislation, but if it take such place — such legal document should not be adopted, and the adopted one should be abolished immediately as illegal, that contradicts with effective Constitution of Ukraine. The priority of Constitution of Ukraine is an integral part of legal state, and Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine, President of Ukraine, Constitutional Court, government and judicial authority are in responsible for this.
And, the last one. In spite of democratic and legal customs and traditions in Ukraine are not strong enough, but there are grave historical cultural traditions, heritage, achievements and also appropriate level of people consciousness, desire to build European state, to carry out other positive, irreversible, proactive processes — all these give reasons to affirm that strong legal state will be built in Ukraine.
Legal state in Ukraine, it is objectively necessary form of organization of legal system and functioning of power, individual and various unions, institutions of society on the basis of law, legality and justice.
55
|


 For the first time in Ukraine it was provided for the research studies and teaching of Ukrainian law in its historical development in 1917, in the separate chair of Kyiv university. Because of the civil war it was impossible to develop its activity, all the more of emigration of the majority of professorate.
Scientific- practical conference of historians and theorists of law took place in Kharkiv in 1957. It admitted the necessity to include the special course of history of statehood and law of national republics to the curriculum of law schools.
During the last 70-th codes of laws and different compilations of statutes, especially government regulations, decrees of the Presidium of the Verkhovna Rada, shorthand records of the sessions of the Verkhovna Rada of the republic had been published constantly. Since publishing of the last years the most informative importance had «Systematic collection of current legislation of USSR» and «Code of statutes of Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic».
At present stage of the development of the Ukrainian Studies it needs by force of professional institutes of Academy of Science of Ukraine, law schools to provide with urgent necessities of scientific treatment problems of theory and history of national law, to increase the publication of current sources of Ukrainian law, monuments of legal culture, to publish the best researches of foreign scientists etc.
By the customary regulation it has been established the order of conclusion of exchange contracts, sales contracts, also the order to use common meadows, water, forest etc.
For the first time in Ukraine it was provided for the research studies and teaching of Ukrainian law in its historical development in 1917, in the separate chair of Kyiv university. Because of the civil war it was impossible to develop its activity, all the more of emigration of the majority of professorate.
Scientific- practical conference of historians and theorists of law took place in Kharkiv in 1957. It admitted the necessity to include the special course of history of statehood and law of national republics to the curriculum of law schools.
During the last 70-th codes of laws and different compilations of statutes, especially government regulations, decrees of the Presidium of the Verkhovna Rada, shorthand records of the sessions of the Verkhovna Rada of the republic had been published constantly. Since publishing of the last years the most informative importance had «Systematic collection of current legislation of USSR» and «Code of statutes of Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic».
At present stage of the development of the Ukrainian Studies it needs by force of professional institutes of Academy of Science of Ukraine, law schools to provide with urgent necessities of scientific treatment problems of theory and history of national law, to increase the publication of current sources of Ukrainian law, monuments of legal culture, to publish the best researches of foreign scientists etc.
By the customary regulation it has been established the order of conclusion of exchange contracts, sales contracts, also the order to use common meadows, water, forest etc.
 In the field of criminal law it is known such cases as private war, fire and water ordeal (so-called «Divine justice»), compensation for damaging words, assault and battery to the health or human honour, property etc.
In the customary law of the Eastern Slavs there was no division into separate institutions, especially as fields of law. In their legal awareness the notion of law combined for the most part with the notion of honesty and conscience, justice and brotherhood, equality and truth. All rules of conduct are recognized by one notion, «Law Rus».
In the conditions of powerful development and extension of international relations of Ukraine-Rus with other countries conventional rules could not satisfy the increasing requirements of social and political life. At the same time it has been appearing new law sources in the order of initiative development of princely legislation by the need of conclusion of interprincely and intergovernmental contracts and treaties.
In due course the process of legislation gets complicated: new statutes and prince’s lessons are proclaimed in towns, districts for the holidays. The most important of them are concentrated in the central authorities, formed and systematized compilations of legal norms.
In the field of criminal law it is known such cases as private war, fire and water ordeal (so-called «Divine justice»), compensation for damaging words, assault and battery to the health or human honour, property etc.
In the customary law of the Eastern Slavs there was no division into separate institutions, especially as fields of law. In their legal awareness the notion of law combined for the most part with the notion of honesty and conscience, justice and brotherhood, equality and truth. All rules of conduct are recognized by one notion, «Law Rus».
In the conditions of powerful development and extension of international relations of Ukraine-Rus with other countries conventional rules could not satisfy the increasing requirements of social and political life. At the same time it has been appearing new law sources in the order of initiative development of princely legislation by the need of conclusion of interprincely and intergovernmental contracts and treaties.
In due course the process of legislation gets complicated: new statutes and prince’s lessons are proclaimed in towns, districts for the holidays. The most important of them are concentrated in the central authorities, formed and systematized compilations of legal norms.
 At the same time the legal church situation in the state, priesthood and other church people was determined except by the Greek Church legal proposition also there was the princely legislation, which took legal shape of church regulations. From six statutes known today there were three which fell within the Ukrainian church: the prince’s Volodymyr Church Statutes, the prince’s Yaroslav Church Statutes and the prince’s Mstyslav Kyivsky Church Statutes. The main content of these princes’s comes to the determination of the church place in the state, subordinacy of church people of the Church court, church right to so-called «tithe».
At the same time the legal church situation in the state, priesthood and other church people was determined except by the Greek Church legal proposition also there was the princely legislation, which took legal shape of church regulations. From six statutes known today there were three which fell within the Ukrainian church: the prince’s Volodymyr Church Statutes, the prince’s Yaroslav Church Statutes and the prince’s Mstyslav Kyivsky Church Statutes. The main content of these princes’s comes to the determination of the church place in the state, subordinacy of church people of the Church court, church right to so-called «tithe».
 It is important for conception of Ukrainian law of that time there are legal internationality contracts that were concluded by the princes with foreign countries, especially with Greeks and Germans. In the ancient times international contracts based themselves principally on municipal law\ customs, traditions, statutes, laws\ and could make new forms of statutes, which reconciled some parts of inter-state agreement relations and had public nature.
Law of that time has not known the division into different branches, determined the strict limit between crime and civil offence, criminal law and civil law yet.
It is important for conception of Ukrainian law of that time there are legal internationality contracts that were concluded by the princes with foreign countries, especially with Greeks and Germans. In the ancient times international contracts based themselves principally on municipal law\ customs, traditions, statutes, laws\ and could make new forms of statutes, which reconciled some parts of inter-state agreement relations and had public nature.
Law of that time has not known the division into different branches, determined the strict limit between crime and civil offence, criminal law and civil law yet.
 Amid the crimes especially dangerous were encroachment on prince’s power, breaking faith, participation in revolt, crimes against the faith and church. The gravest and the most dangerous crimes against the personality were a murder, mutilation, slashing and batterery, property destruction. Farther on there were such kinds of crimes as contumeliousy, contempt, damaging of other’s property.
A proceeding formed historically and was adversarial-incriminating. Different parts in the lawsuit were equal, and therefore their collected physical evidence, witnesses and also conducted special investigation proceedings such as «persecution track», «code» and others by themselves.
It is known that the successor of Kievan Rus in Ukraine was the Galicia-Volyn principality — the state, whose formation dates refer to the second half of the 11th century.
In addition to separate sources of local law, in Ukraine there act and were effective normative acts of foreign extraction, including Law Code of Casimir of 1468, — at the same time both the Polish king and the grand Lithuanian prince, Sejm decrees and constitutions of Rich Pospolyta such as «Ustav na Voloki» 1557, «The Lithuanian Statute» three editions (1529, 1566, 1588), differ
ent re-makings of collection of urban self-government rights (so called Magdeburg law), «Zertsalo of Saxons» etc.
Amid the crimes especially dangerous were encroachment on prince’s power, breaking faith, participation in revolt, crimes against the faith and church. The gravest and the most dangerous crimes against the personality were a murder, mutilation, slashing and batterery, property destruction. Farther on there were such kinds of crimes as contumeliousy, contempt, damaging of other’s property.
A proceeding formed historically and was adversarial-incriminating. Different parts in the lawsuit were equal, and therefore their collected physical evidence, witnesses and also conducted special investigation proceedings such as «persecution track», «code» and others by themselves.
It is known that the successor of Kievan Rus in Ukraine was the Galicia-Volyn principality — the state, whose formation dates refer to the second half of the 11th century.
In addition to separate sources of local law, in Ukraine there act and were effective normative acts of foreign extraction, including Law Code of Casimir of 1468, — at the same time both the Polish king and the grand Lithuanian prince, Sejm decrees and constitutions of Rich Pospolyta such as «Ustav na Voloki» 1557, «The Lithuanian Statute» three editions (1529, 1566, 1588), differ
ent re-makings of collection of urban self-government rights (so called Magdeburg law), «Zertsalo of Saxons» etc.

 All sources of law acted in reciprocity, sometimes to put standards of urban law into the foundation of causes’ consideration.
Famous Ukrainian academic scientist D. Bataliy affirmed that there were not even two cities in Ukraine where the sum of the Magdeburg laws was the same and that was the reason to give the city all rights for self-government and significance of the city.
In the Middle Dnieper regions, so called Cossacks and their battle centre the Zaporizhian Sich, has appeared as the result of reinforcement of socio-economic, political and legal, and national-religious oppression of Ukrainians.
Cossacks’ self-acting, as the whole system of organs of military and administrative government had the opportunity to act and provide such inner and outside functions which are peculiar and inherent for state.
People’s Liberation War in 1648–1654 allowed forming the most important stage of revival of national statehood in Ukraine.
During the revival of national statehood in Ukraine there appeared distinctive system of law and court, the foundation of which was the customary law of Zaporizhian Sich, especially those standards of this law, which during the People’s Liberation War regulated military and administrative organization and administration, rights and duties of Cossack officers, legal procedure etc.
At the same time the customary law of Zaporizhian Sich was supplemented by acts of the law of local military and administrative government, as far as it was considered national law and it was the most prestige among people, and was protected by government and national rites, traditions and even got specific name «Cossack law». Also it completely formed ambushes for the future and became the basis of Hetman law.
Despite the complexity and contradiction of real legal status in Ukraine as a part of Russia, Hetman legal system existed until 1840–1842 years.
At that time a lot of regulations were out of date and often contradicted each other, duplicated specific legal provisions etc. The main concern was that the actual legal system Hetman did not only match, but sometimes even contradicted to the legal system of Russia, its imperial claims.
Also we should notice the fact that social order landowners Hetman was done most fully and carefully only during the second official codification of 1750–1758 years, when on the instruction of hetman K. Rozumovsky candidate members of the General Military Court F. Chuykevych worked out collection of legal norms and legal proceedings under the title «Judgment and punishment in the Little Russian rights».
In history of Ukraine law there are two very similar in form but very opposite to the content of legal interest.
All sources of law acted in reciprocity, sometimes to put standards of urban law into the foundation of causes’ consideration.
Famous Ukrainian academic scientist D. Bataliy affirmed that there were not even two cities in Ukraine where the sum of the Magdeburg laws was the same and that was the reason to give the city all rights for self-government and significance of the city.
In the Middle Dnieper regions, so called Cossacks and their battle centre the Zaporizhian Sich, has appeared as the result of reinforcement of socio-economic, political and legal, and national-religious oppression of Ukrainians.
Cossacks’ self-acting, as the whole system of organs of military and administrative government had the opportunity to act and provide such inner and outside functions which are peculiar and inherent for state.
People’s Liberation War in 1648–1654 allowed forming the most important stage of revival of national statehood in Ukraine.
During the revival of national statehood in Ukraine there appeared distinctive system of law and court, the foundation of which was the customary law of Zaporizhian Sich, especially those standards of this law, which during the People’s Liberation War regulated military and administrative organization and administration, rights and duties of Cossack officers, legal procedure etc.
At the same time the customary law of Zaporizhian Sich was supplemented by acts of the law of local military and administrative government, as far as it was considered national law and it was the most prestige among people, and was protected by government and national rites, traditions and even got specific name «Cossack law». Also it completely formed ambushes for the future and became the basis of Hetman law.
Despite the complexity and contradiction of real legal status in Ukraine as a part of Russia, Hetman legal system existed until 1840–1842 years.
At that time a lot of regulations were out of date and often contradicted each other, duplicated specific legal provisions etc. The main concern was that the actual legal system Hetman did not only match, but sometimes even contradicted to the legal system of Russia, its imperial claims.
Also we should notice the fact that social order landowners Hetman was done most fully and carefully only during the second official codification of 1750–1758 years, when on the instruction of hetman K. Rozumovsky candidate members of the General Military Court F. Chuykevych worked out collection of legal norms and legal proceedings under the title «Judgment and punishment in the Little Russian rights».
In history of Ukraine law there are two very similar in form but very opposite to the content of legal interest.

 This is «The extract of Little Russian rights» which was worked out on the instruction of governor of Little Russia P. Rumiantseva, Little Board secretary O. Bezborodko in 1767 and «The extract of the decrees, regulations and institutions … Senate» of Russia in 1786.
In the last decade of the 17th century abolished by Catherine II and restored by Paul I «prior law on the judiciary and judicial proceedings outdated in Ukraine, that’s why they did not correspond its colonial situation in the Russian Empire and new conditions of socio-economical development of society.
Attempts at reforming the law of Ukraine and the whole empire has occurred in the first half of the 19th century. But they actually have already broken against the imperial policy of Alexander I and Nicholas I, who ruled the country «on the model rules of Grandmother Catherine» strictly looking at the fact that not only the letter but the spirit of her legislation were not changed.
In the period of formation of a unified legal system of the Russian Empire in 1840 in Ukraine was extended operation of law «Code Laws Empire» first, and in 1842 — the second version of the same Code. During 1824–183 5 was abolished action of Magdeburg law and implemented in urban management and proceedings of the imperial «Charter cities» 1875.
For the development rights of Galicia, Northern Bukovina and Transcarpathia affected their being a part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. In 1753 in Austria it has already been created a special commission that was supposed to take steps to unify the empire right to liquidate its particularism, to develop a unified empire codes for different spheres of justice. For approval new codes in Galicia and Bukovina there operated customary law and sources of Polish law.
Since the late 17th century, at first in Galicia and later throughout the empire there began its criminal code in 1787, and since 1788 — the statute of criminal crimes. Present criminal code provided for severe punishment as death by hanging and the procedural code had the inquisitorial nature of the process, without a lawyer. Sentences were considered final and performed no later than 24 hours after their removal. These were the so-called «sudden courts».
The autocracy was eliminated after the victory of the bourgeois-democratic revolution in February 1917.
Therefore, 4 ( 17) March, 1917 there took place the Congress with representatives of the revolutionary parties, social movements, institutions and societies, which created the Central Council — nationwide coordination center. M. Hrushevsky, famous scientist and public-political figure, was elected as a chairman by the Central Council.
Proclamation of an independent Ukrainian National Republic was an extremely important decision and of course, it was noticeable in international relations. That’s why Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria and Turkey immediately concluded a peace agreement with Ukraine on January 14 ( 27), 1918. Also, sovereign Ukrainian state was recognized by such powerful states like Britain, France, USA, Japan, China, Finland, Poland, Romania, and later — Hungary, Czechoslovakia, the Vatican and other countries in the world. To keep the authority the Central Council requested military assistance from Germany and Austria-Hungary. But the revolution turned into a civil war, which was complicated by the intervention of outside powers — Germany and the states of Atlanta from the West and Soviet Russia — from the East.
The legal system of Western People’s Republic was defined by the law from November 21, 1918. Judicial functions were performed by county circuit courts and Supreme Court.
The legal system of the Soviet Ukraine began to form from the day of its proclamation, virtually from the day of the first All-Ukrainian Soviet Congress of Workers, Peasants and Soldiers’ Deputies. Basic rights have been secured by the Constitution of the USSR in 1919.
But with the entry of Ukraine into the USSR in the next years, especially in strengthening the administrative-command system
of centralized management, national moments in the development of law has already ceased to be counted.
This is «The extract of Little Russian rights» which was worked out on the instruction of governor of Little Russia P. Rumiantseva, Little Board secretary O. Bezborodko in 1767 and «The extract of the decrees, regulations and institutions … Senate» of Russia in 1786.
In the last decade of the 17th century abolished by Catherine II and restored by Paul I «prior law on the judiciary and judicial proceedings outdated in Ukraine, that’s why they did not correspond its colonial situation in the Russian Empire and new conditions of socio-economical development of society.
Attempts at reforming the law of Ukraine and the whole empire has occurred in the first half of the 19th century. But they actually have already broken against the imperial policy of Alexander I and Nicholas I, who ruled the country «on the model rules of Grandmother Catherine» strictly looking at the fact that not only the letter but the spirit of her legislation were not changed.
In the period of formation of a unified legal system of the Russian Empire in 1840 in Ukraine was extended operation of law «Code Laws Empire» first, and in 1842 — the second version of the same Code. During 1824–183 5 was abolished action of Magdeburg law and implemented in urban management and proceedings of the imperial «Charter cities» 1875.
For the development rights of Galicia, Northern Bukovina and Transcarpathia affected their being a part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. In 1753 in Austria it has already been created a special commission that was supposed to take steps to unify the empire right to liquidate its particularism, to develop a unified empire codes for different spheres of justice. For approval new codes in Galicia and Bukovina there operated customary law and sources of Polish law.
Since the late 17th century, at first in Galicia and later throughout the empire there began its criminal code in 1787, and since 1788 — the statute of criminal crimes. Present criminal code provided for severe punishment as death by hanging and the procedural code had the inquisitorial nature of the process, without a lawyer. Sentences were considered final and performed no later than 24 hours after their removal. These were the so-called «sudden courts».
The autocracy was eliminated after the victory of the bourgeois-democratic revolution in February 1917.
Therefore, 4 ( 17) March, 1917 there took place the Congress with representatives of the revolutionary parties, social movements, institutions and societies, which created the Central Council — nationwide coordination center. M. Hrushevsky, famous scientist and public-political figure, was elected as a chairman by the Central Council.
Proclamation of an independent Ukrainian National Republic was an extremely important decision and of course, it was noticeable in international relations. That’s why Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria and Turkey immediately concluded a peace agreement with Ukraine on January 14 ( 27), 1918. Also, sovereign Ukrainian state was recognized by such powerful states like Britain, France, USA, Japan, China, Finland, Poland, Romania, and later — Hungary, Czechoslovakia, the Vatican and other countries in the world. To keep the authority the Central Council requested military assistance from Germany and Austria-Hungary. But the revolution turned into a civil war, which was complicated by the intervention of outside powers — Germany and the states of Atlanta from the West and Soviet Russia — from the East.
The legal system of Western People’s Republic was defined by the law from November 21, 1918. Judicial functions were performed by county circuit courts and Supreme Court.
The legal system of the Soviet Ukraine began to form from the day of its proclamation, virtually from the day of the first All-Ukrainian Soviet Congress of Workers, Peasants and Soldiers’ Deputies. Basic rights have been secured by the Constitution of the USSR in 1919.
But with the entry of Ukraine into the USSR in the next years, especially in strengthening the administrative-command system
of centralized management, national moments in the development of law has already ceased to be counted.
 New direction and forms of law in Ukraine determined the effects of long scientific debate in the 50 s.
On the basis of the adopted and enacted legislation in the 60–70s years there was held the second general codification of Ukraine law, that had resulted in the creation of new codes of the Republic, which in the late 70’s — early 80’s were brought into compliance with new provisions of the Constitution of the USSR in 1977 and the Constitution of the Republic USSR in 1978.
Ukrainian law on the present stage of development (from 1990 till 2010)
New direction and forms of law in Ukraine determined the effects of long scientific debate in the 50 s.
On the basis of the adopted and enacted legislation in the 60–70s years there was held the second general codification of Ukraine law, that had resulted in the creation of new codes of the Republic, which in the late 70’s — early 80’s were brought into compliance with new provisions of the Constitution of the USSR in 1977 and the Constitution of the Republic USSR in 1978.
Ukrainian law on the present stage of development (from 1990 till 2010)
 Present stage of revival of national Ukrainian law relates to the first free elections of urban Councils and Verkhovna Rada, which were in March 1990. Thus, it was formed new parliament, which later began to take into its hands all economical and political power and became firmly established as the only legislative organ of URSR.
Democratic bloc of public organizations got approximately quarter (from 450) mandates in Verkhovna Rada and on July 16th, 1990 won prominent victory in parliament. According to its initiative Vekhovna Rada signed «Declaration about state sovereignty of Ukraine»; as the result of this action the state sovereignty was proclaimed as the supremacy, independence, plenitude and indivisibility of power of Republic within the limits of her territory, independence and equality in its external relations.
«People of Ukraine, — declares this legal act, — are the only source of state power in Republic. State power accomplishes by the principle of her dividing into legislative, executive and judicial. Any violent actions against the national state system of Ukraine from the side of political parties, public organizations, other groupments or individuals are pursued on a law. The state of Ukraine acknowledges advantage of common to all mankind values above class, priority of confessedly norms of international law above norms of domestic right. Declaration, which is underlined in a final part of act, is a foundation for new Constitution, different laws of Ukraine and determines positions of Republic at the mode of international agreements».
Declaration from July 16th, 1990 is a foundation for development of current legislation and forming of new legal system of Ukraine.
The attempt of putsch on August 18–21, 1991 accelerated disintegration of the USSR, but it did not influence on the change of the accepted course of democratic transformations in Ukraine. «As well as before, — declared on Ukrainian TV future president of Ukraine L. Kuchma, — we must go on the way of democracy, legality, law and order, observance of constitutional norms».
Expressing will of people, Verkhovna Rada of Respublic on August 24th, 1991 signed «Act of proclamation of independence of Ukraine». Where, in particular, it is indicated: «… — on self-determination, foreseen by UN Charter and other international documents, — realizing the “Declaration about state sovereignty of Ukraine», Vekhovna Rada proclaimed the independence of Ukraine and creation of independent Ukrainian state — Ukraine, the territory of which is indivisible and inviolable. From this time, — the act concluded, — on the territory of Ukraine operate exceptionally Constitution and laws of Ukraine.
Present stage of revival of national Ukrainian law relates to the first free elections of urban Councils and Verkhovna Rada, which were in March 1990. Thus, it was formed new parliament, which later began to take into its hands all economical and political power and became firmly established as the only legislative organ of URSR.
Democratic bloc of public organizations got approximately quarter (from 450) mandates in Verkhovna Rada and on July 16th, 1990 won prominent victory in parliament. According to its initiative Vekhovna Rada signed «Declaration about state sovereignty of Ukraine»; as the result of this action the state sovereignty was proclaimed as the supremacy, independence, plenitude and indivisibility of power of Republic within the limits of her territory, independence and equality in its external relations.
«People of Ukraine, — declares this legal act, — are the only source of state power in Republic. State power accomplishes by the principle of her dividing into legislative, executive and judicial. Any violent actions against the national state system of Ukraine from the side of political parties, public organizations, other groupments or individuals are pursued on a law. The state of Ukraine acknowledges advantage of common to all mankind values above class, priority of confessedly norms of international law above norms of domestic right. Declaration, which is underlined in a final part of act, is a foundation for new Constitution, different laws of Ukraine and determines positions of Republic at the mode of international agreements».
Declaration from July 16th, 1990 is a foundation for development of current legislation and forming of new legal system of Ukraine.
The attempt of putsch on August 18–21, 1991 accelerated disintegration of the USSR, but it did not influence on the change of the accepted course of democratic transformations in Ukraine. «As well as before, — declared on Ukrainian TV future president of Ukraine L. Kuchma, — we must go on the way of democracy, legality, law and order, observance of constitutional norms».
Expressing will of people, Verkhovna Rada of Respublic on August 24th, 1991 signed «Act of proclamation of independence of Ukraine». Where, in particular, it is indicated: «… — on self-determination, foreseen by UN Charter and other international documents, — realizing the “Declaration about state sovereignty of Ukraine», Vekhovna Rada proclaimed the independence of Ukraine and creation of independent Ukrainian state — Ukraine, the territory of which is indivisible and inviolable. From this time, — the act concluded, — on the territory of Ukraine operate exceptionally Constitution and laws of Ukraine.
 In new conditionals of alteration of economy of Ukraine, creating new national independent state, Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine conducts wide scale, legislative activity; more clearly determines the legal system of new society.
In this work an important value had «The law about legal continuity of Ukraine», accepted on September 12th, 1991. Before acceptance of new Constitution of Ukraine, in this law was determined that on the territory o f Ukraine operates Constitution (main law) of URSR. Laws of URSR and other acts, accepted by Verkhovna Rada of URSR, operate on the territory of Ukraine, as they do not contradict laws, which were signed after proclamation of independence of Ukraine. Ukraine confirmed its duties on the international agreements of the USSR, if they do not contradict with the Constitution of Ukraine and interests of republic. Independent Ukraine does not take the responsibility on credit agreements made without its consent after July 1st, 1991.
In relation to the legislation of the USSR Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine by a decision from September 12th, 1991 «About order of temporal action on territory of Ukraine of separate acts of legislation of the USSR» set that to the acceptance of corresponding acts of legislation of Ukraine on the territory of republic are applied the acts of legislation of the USSR on questions that are not well-regulated by the legislation of Ukraine, on condition that they do not contradict with a Constitution and laws of Ukraine.
Thus, at that time were formed the newest visible lines of modern national legal system of Ukraine. Today it continues to create farther. That’s great that Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine at this time takes under its jurisdiction everything that belongs to the sovereign state, beginning with borders, army, creating new laws on earth, entrepreneurial activity, human rights and surrounds its environment. Certainly, the process of lawmaking requires clearer, considered decision. As the result of this, Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine creates the law with important, but not always near-term problems of alteration of life of society and creation of legal state of Ukraine.
New age of 19th century requires new approaches and high quality of law-making, adoption of such laws which must assert and provide supremacy of right, justice, legality and other ideals of new generation of the Ukrainian people. Thus, on the stage of Ukrainian creation of the state, it was made right and effective beginning.
Gnosiological and view-methodological principles of realization of ideas of the legal state in Ukraine
Analysis of current legal system, legislation and development of state-building processes in Ukraine since independence (1991–2011 — almost 20 years), it shows us that in state is begun the process of forming of constitutionally-legal principles and mechanisms of development of social and legal state. Among the most meaningful achievements in the sphere of state-building activity there are:
revival of liberal-democratic traditions of constitutionalism (art. 1–68 Constitution of Ukraine);
laying the foundation of parliamentarism (art. 75–101 Constitution of Ukraine);
realization of principle of distribution of power (art. 6 Constitution of Ukraine);
process of reformation of the judicial system (art. 124–131 Constitution of Ukraine);
realization of transformation of the national system of legislation;
forming of positive tendencies in the estimation of human rights and freedoms and their protection
Restructuring (just with grave disadvantages and problems) of electoral laws;
Formation of Constitutional Court, Higher Council of Justice, setting as principle of legal platform and machineries of national security, activity of judicial proceeding, armed forces and protection of state borders;
Formation of foundations for public organization functioning, movements, television, non-state security service as basic elements of civil society.
Certainly this list can be continued, but main task for us today is to consolidate existing process, to develop and improve conceptions, doctrines, ideas, laws, other institutes and provide for real machineries of formation of legal state. Everyone has to understand that it is impossible to form a legal state, coming only to nothing more than adoption of laws.
Main problems of forming legal state in Ukraine come to that under conditions of pluralism of opinions, ideologies, changing of elites and power — sense and content of legal state idea can disagree fundamentally and even interpret in a different way, but of course it is not promote for harmonious state development. That’s why it should be promoted of the development of statehood in Ukraine.
At the same time principal things are permanent — Ukrainian legal state in spite of its special features, keeping its statehood. And it means that:
It does not identify with society and another system of special-political organization;
Except its own, specific features it has general signs;
It is committed with public authority, and it is an official representative of all social stratums;
It has apparatus of administration and coercion ;
It has system of legal measures in contrast to non-state organizations;
It has sovereignty that is shown in its supremacy concerning all another non-state organizations and all citizens.
All listed signs and features hereinbefore are general for any state, which are typical only for social, legal state. Among such distinctive important settings and guides the most important, in our opinion, are:
Right as a measure of equality, justice and liberty that dominates in all spheres of society;
Law acts not only for citizens but for all officers, government employees, organs and institutions of state authority and municipal government, while the country as a whole;
state authority functions on a footing of Constitution of Ukraine and effects by the principle of its division into legislative, executive and judicial authorities and it is implemented on the basis of functioning of “system of checks and balances” among them;
Rights, liberties and individual interests are indefeasible, and state guarantees their realization and secures them;
There is a reciprocal state and person responsibility;
Organized effective monitoring of legality (laws, decrees, regulations, instructions, orders etc);
highly effective activity of law enforcement and law courts to enforce rule of law, ensure the protection of human rights and liberties;
solution of conflicts and controversial questions only in court instances because the justice is accomplished only by law courts in Ukraine.
In new conditionals of alteration of economy of Ukraine, creating new national independent state, Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine conducts wide scale, legislative activity; more clearly determines the legal system of new society.
In this work an important value had «The law about legal continuity of Ukraine», accepted on September 12th, 1991. Before acceptance of new Constitution of Ukraine, in this law was determined that on the territory o f Ukraine operates Constitution (main law) of URSR. Laws of URSR and other acts, accepted by Verkhovna Rada of URSR, operate on the territory of Ukraine, as they do not contradict laws, which were signed after proclamation of independence of Ukraine. Ukraine confirmed its duties on the international agreements of the USSR, if they do not contradict with the Constitution of Ukraine and interests of republic. Independent Ukraine does not take the responsibility on credit agreements made without its consent after July 1st, 1991.
In relation to the legislation of the USSR Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine by a decision from September 12th, 1991 «About order of temporal action on territory of Ukraine of separate acts of legislation of the USSR» set that to the acceptance of corresponding acts of legislation of Ukraine on the territory of republic are applied the acts of legislation of the USSR on questions that are not well-regulated by the legislation of Ukraine, on condition that they do not contradict with a Constitution and laws of Ukraine.
Thus, at that time were formed the newest visible lines of modern national legal system of Ukraine. Today it continues to create farther. That’s great that Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine at this time takes under its jurisdiction everything that belongs to the sovereign state, beginning with borders, army, creating new laws on earth, entrepreneurial activity, human rights and surrounds its environment. Certainly, the process of lawmaking requires clearer, considered decision. As the result of this, Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine creates the law with important, but not always near-term problems of alteration of life of society and creation of legal state of Ukraine.
New age of 19th century requires new approaches and high quality of law-making, adoption of such laws which must assert and provide supremacy of right, justice, legality and other ideals of new generation of the Ukrainian people. Thus, on the stage of Ukrainian creation of the state, it was made right and effective beginning.
Gnosiological and view-methodological principles of realization of ideas of the legal state in Ukraine
Analysis of current legal system, legislation and development of state-building processes in Ukraine since independence (1991–2011 — almost 20 years), it shows us that in state is begun the process of forming of constitutionally-legal principles and mechanisms of development of social and legal state. Among the most meaningful achievements in the sphere of state-building activity there are:
revival of liberal-democratic traditions of constitutionalism (art. 1–68 Constitution of Ukraine);
laying the foundation of parliamentarism (art. 75–101 Constitution of Ukraine);
realization of principle of distribution of power (art. 6 Constitution of Ukraine);
process of reformation of the judicial system (art. 124–131 Constitution of Ukraine);
realization of transformation of the national system of legislation;
forming of positive tendencies in the estimation of human rights and freedoms and their protection
Restructuring (just with grave disadvantages and problems) of electoral laws;
Formation of Constitutional Court, Higher Council of Justice, setting as principle of legal platform and machineries of national security, activity of judicial proceeding, armed forces and protection of state borders;
Formation of foundations for public organization functioning, movements, television, non-state security service as basic elements of civil society.
Certainly this list can be continued, but main task for us today is to consolidate existing process, to develop and improve conceptions, doctrines, ideas, laws, other institutes and provide for real machineries of formation of legal state. Everyone has to understand that it is impossible to form a legal state, coming only to nothing more than adoption of laws.
Main problems of forming legal state in Ukraine come to that under conditions of pluralism of opinions, ideologies, changing of elites and power — sense and content of legal state idea can disagree fundamentally and even interpret in a different way, but of course it is not promote for harmonious state development. That’s why it should be promoted of the development of statehood in Ukraine.
At the same time principal things are permanent — Ukrainian legal state in spite of its special features, keeping its statehood. And it means that:
It does not identify with society and another system of special-political organization;
Except its own, specific features it has general signs;
It is committed with public authority, and it is an official representative of all social stratums;
It has apparatus of administration and coercion ;
It has system of legal measures in contrast to non-state organizations;
It has sovereignty that is shown in its supremacy concerning all another non-state organizations and all citizens.
All listed signs and features hereinbefore are general for any state, which are typical only for social, legal state. Among such distinctive important settings and guides the most important, in our opinion, are:
Right as a measure of equality, justice and liberty that dominates in all spheres of society;
Law acts not only for citizens but for all officers, government employees, organs and institutions of state authority and municipal government, while the country as a whole;
state authority functions on a footing of Constitution of Ukraine and effects by the principle of its division into legislative, executive and judicial authorities and it is implemented on the basis of functioning of “system of checks and balances” among them;
Rights, liberties and individual interests are indefeasible, and state guarantees their realization and secures them;
There is a reciprocal state and person responsibility;
Organized effective monitoring of legality (laws, decrees, regulations, instructions, orders etc);
highly effective activity of law enforcement and law courts to enforce rule of law, ensure the protection of human rights and liberties;
solution of conflicts and controversial questions only in court instances because the justice is accomplished only by law courts in Ukraine.
 At the same time, further development of legal state in Ukraine should continue to realize by the way of formed transformations and in the majority of formal features, in other words to be implemented in fundamental ideological creative principles. Among the most significant and actual directions of such perspective are:
The formation of civil society as a foundation of legal state. The civil society can ensure free and comprehensive development of personality, functioning of public institutions, free accession to the information, election, opposition, multi-party system etc.
Fundamental achievements of scientists in the field of law affirm that only civil society can oppose to the criminalized and corrupted in all society, processes of the usurpation of power, confrontation of democratic processes.
The construction of legal state is linked objectively with consolidation of democratic processes, reforms and traditions of functioning of power in Ukraine, in as much as the embodiment of democratic principles forms precondition of social equality and justice. At the same time democratic traditions in Ukraine which are been forming, still feeble and their fixing and development are prolonged and very important process for a person, authority and society. The pledge of these processes is a preservation of free election, formation of democratic political regime, liberty of mass media, clarity and farsightedness of politicians, patriotism, devotion to the national idea, preservation and revival of national customs, traditions, spirituality, social heritage etc, which will become almost the most important pledge of development of harmonious legal state in the near future.
Development of legal state depends directly on the level, range, systemic economic policy and state creative reforms.
At the same time, further development of legal state in Ukraine should continue to realize by the way of formed transformations and in the majority of formal features, in other words to be implemented in fundamental ideological creative principles. Among the most significant and actual directions of such perspective are:
The formation of civil society as a foundation of legal state. The civil society can ensure free and comprehensive development of personality, functioning of public institutions, free accession to the information, election, opposition, multi-party system etc.
Fundamental achievements of scientists in the field of law affirm that only civil society can oppose to the criminalized and corrupted in all society, processes of the usurpation of power, confrontation of democratic processes.
The construction of legal state is linked objectively with consolidation of democratic processes, reforms and traditions of functioning of power in Ukraine, in as much as the embodiment of democratic principles forms precondition of social equality and justice. At the same time democratic traditions in Ukraine which are been forming, still feeble and their fixing and development are prolonged and very important process for a person, authority and society. The pledge of these processes is a preservation of free election, formation of democratic political regime, liberty of mass media, clarity and farsightedness of politicians, patriotism, devotion to the national idea, preservation and revival of national customs, traditions, spirituality, social heritage etc, which will become almost the most important pledge of development of harmonious legal state in the near future.
Development of legal state depends directly on the level, range, systemic economic policy and state creative reforms.
 It is necessary to finish constitutional reform in the society on a legal footing to guarantee its implementation arrangements and in such way to paragraph about its violation in adoption of any law (tax code, labour code or other normative act). It is necessary to remedy through a referendum a polity in Ukraine, to pass the law on the responsibility of President, government, deputies of all levels; to conduct wide discussions about their sense, results etc. It needs honestly, openly, objectively to inform population about real, economic, financial, political, secure situation in the country. The authority must be politically responsible for non-professional actions of government officials, their decision-making and results. Legal state it is not only democratic but also social and sovereign country.
Legal state, it is first of all constitutional state.
Constitution of Ukraine — is the main law of legal state, it is a general, legal, moral model of society. No one other law, code, normative act should not and cannot contradict with Constitution of Ukraine, to create collisions in current legislation, but if it take such place — such legal document should not be adopted, and the adopted one should be abolished immediately as illegal, that contradicts with effective Constitution of Ukraine. The priority of Constitution of Ukraine is an integral part of legal state, and Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine, President of Ukraine, Constitutional Court, government and judicial authority are in responsible for this.
And, the last one. In spite of democratic and legal customs and traditions in Ukraine are not strong enough, but there are grave historical cultural traditions, heritage, achievements and also appropriate level of people consciousness, desire to build European state, to carry out other positive, irreversible, proactive processes — all these give reasons to affirm that strong legal state will be built in Ukraine.
Legal state in Ukraine, it is objectively necessary form of organization of legal system and functioning of power, individual and various unions, institutions of society on the basis of law, legality and justice.
It is necessary to finish constitutional reform in the society on a legal footing to guarantee its implementation arrangements and in such way to paragraph about its violation in adoption of any law (tax code, labour code or other normative act). It is necessary to remedy through a referendum a polity in Ukraine, to pass the law on the responsibility of President, government, deputies of all levels; to conduct wide discussions about their sense, results etc. It needs honestly, openly, objectively to inform population about real, economic, financial, political, secure situation in the country. The authority must be politically responsible for non-professional actions of government officials, their decision-making and results. Legal state it is not only democratic but also social and sovereign country.
Legal state, it is first of all constitutional state.
Constitution of Ukraine — is the main law of legal state, it is a general, legal, moral model of society. No one other law, code, normative act should not and cannot contradict with Constitution of Ukraine, to create collisions in current legislation, but if it take such place — such legal document should not be adopted, and the adopted one should be abolished immediately as illegal, that contradicts with effective Constitution of Ukraine. The priority of Constitution of Ukraine is an integral part of legal state, and Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine, President of Ukraine, Constitutional Court, government and judicial authority are in responsible for this.
And, the last one. In spite of democratic and legal customs and traditions in Ukraine are not strong enough, but there are grave historical cultural traditions, heritage, achievements and also appropriate level of people consciousness, desire to build European state, to carry out other positive, irreversible, proactive processes — all these give reasons to affirm that strong legal state will be built in Ukraine.
Legal state in Ukraine, it is objectively necessary form of organization of legal system and functioning of power, individual and various unions, institutions of society on the basis of law, legality and justice.